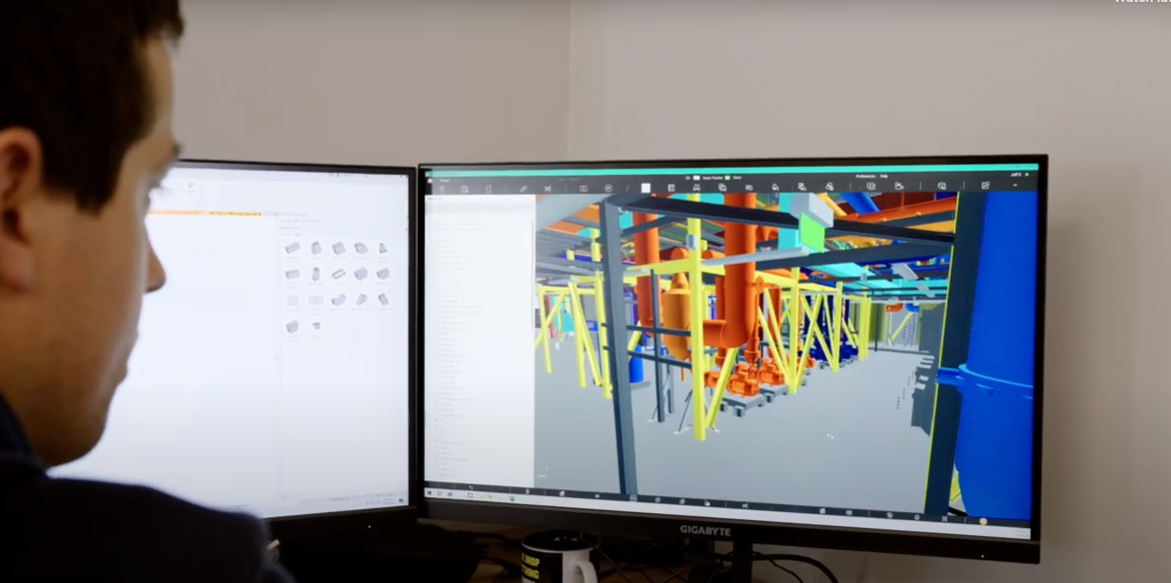
Contractor / Subcontractor | Model interaction for planning
Description
Contractors and subcontractors commonly complete a task analysis before starting work on site. A task analysis describes how the works will be carried out safely and how risks will be managed. Task analysis generally involves explaining step-by-step procedures while identifying hazards and risks.
While task analysis can be viewed as a box-ticking exercise, the real challenge is to recognise the current site situation. Each site has its own challenges that expose people to risk.
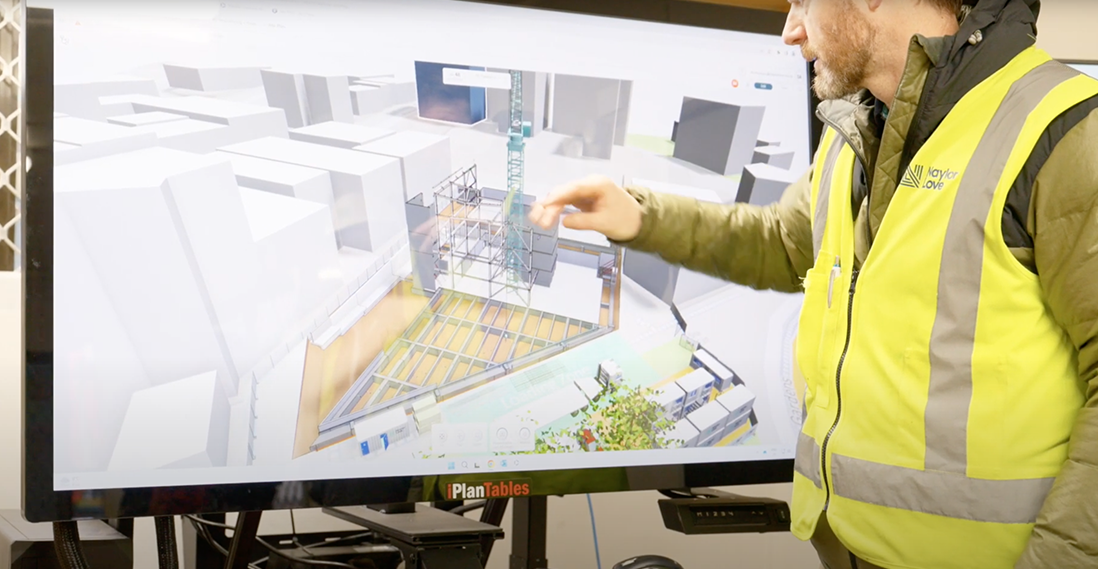
A BIM construction model can transform safe work method statements into construction sequencing animations and simulations that allow users to interact with the placement and movement of personnel, plant and equipment, which the project team can use to identify hazards and assess options for safer delivery.
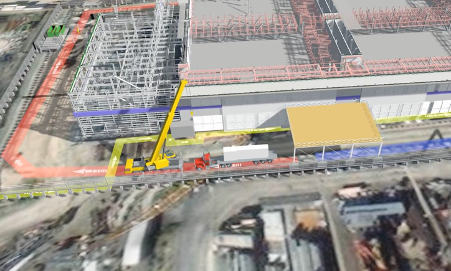
Using the model to validate a crane lift on site
Case studies
Uses and benefits for health and safety
- Enable users to experience real-world challenges and hazards when performing tasks and construction activities, whether it’s by using desktop software, or virtual or augmented reality.
- Improve planning and task analysis, especially for hazardous work activities, such as working in confined spaces, working at height and working near hazardous elements.
- Ensure adequate health and safety protocols are in place by testing safe work method statements against model simulations.
Technology/techniques
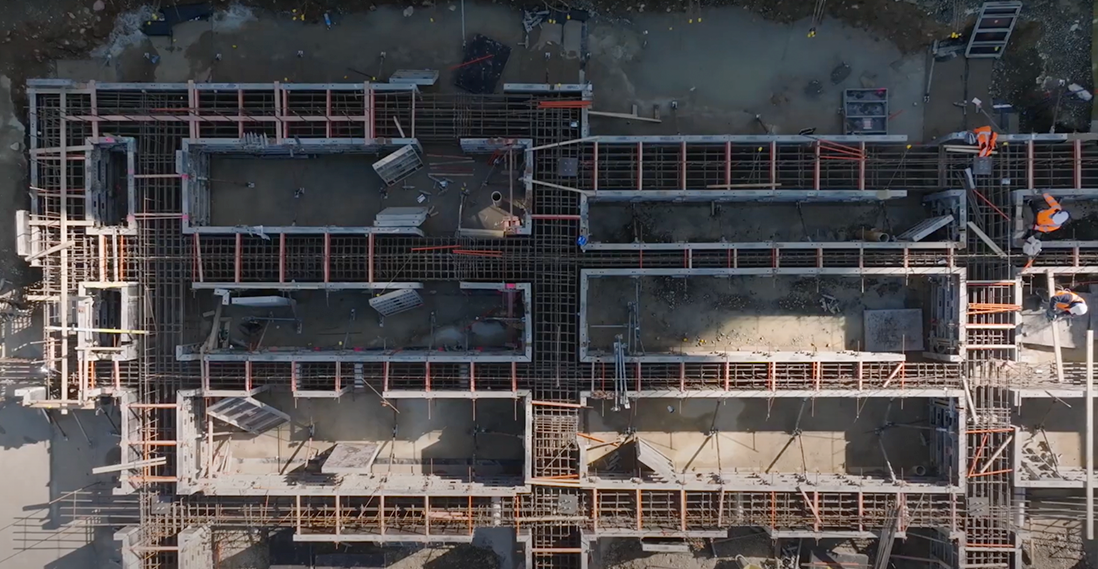
The first step is to make a federated construction model by combining BIM models from all the permanent works and temporary elements. The model can then be used to measure construction clearances while performing works, assess whether there is enough space to carry out works, and ensure work zones are large enough for equipment and installers.
At a minimum, high-risk activities should be planned and simulated in the BIM environment to account for all identified hazards.
Simulations and virtual walk throughs can raise awareness among site personnel, including those who work in other areas or on other project activities. Simulations can also help get buy-in and gather feedback from project stakeholders.
Model/data requirements
Using an interactive model for planning requires BIM models from subcontractors and designers, along with a safe work method statement for activities. The BIM model should include elements used in construction activities, such as cranes, elevated work platforms, and void elements representing restricted zones.
The federated model can incorporate changes and annotations, and be set up with pre-set viewpoints, which enable workers to view task simulations from different angles.
Hardware and software requirements
Hardware suitable for basic CAD work is recommended for small- to medium-sized BIM files (16 GB of RAM for models up to 150 MB). Bigger models (larger than 150 Mb) require a faster processor, graphics card and additional RAM.
Federated models created using an industry federation class (IFC)-based process can be accessed using a range of different software, most of which offer a free viewer.
A federated model created using Autodesk tools can use the free Navisworks Freedom software for viewing.
For cloud-based platforms, such as Revizto or Autodesk’s Construction Cloud, a licence is needed to open and navigate models.
Contract/procurement implications
Model interaction is a common requirement, especially in medium- to large-scale infrastructure and building projects. In addition to health and safety, a federated model can be used in design reviews and spatial planning. Model federation should be included in the BIM brief and priced during procurement.
Roles and responsibilities
| Main contractor |
Manages data exchange and sets up software and licenses for all stakeholders. Also responsible for validating models from trades and designers to ensure the latest information is in the BIM model. |
| Project engineer |
Uses the model to validate the safe work method statement by checking dimensions and clearances. ㅤ |
| Health and safety resource |
Collaborates with the Project Engineer or Supervisor to identify hazards and mitigations. ㅤ |
Training requirements
Model navigation and integration involves opening the model and creating viewpoints that project personnel can use for virtual walk throughs and measurements; these are basic functions of any BIM-based software which staff can learn in an online course or in person via the software vendor.
Most vendors provide one-day courses for their users before the project begins.
Future directions
Planning works using interactive models is likely to become standard practice in the future. Increasingly, safe work method statements are likely to include video clips which show step-by-step instructions on how to carry out the work safely. Using a BIM model as a validation tool is also likely to become an integral part in construction planning.